5️⃣DBMS Architecture 1-level, 2-Level, 3-Level
A Database stores a lot of critical information to access data quickly and securely. Hence it is important to select the correct architecture for efficient data management. DBMS Architecture helps users to get their requests done while connecting to the database. We choose database architecture depending on several factors like the size of the database, number of users, and relationships between the users. There are two types of database models that we generally use, logical model and physical model. Several types of architecture are there in the database which we will deal with in the next section.
Types of DBMS Architecture
There are several types of DBMS Architecture that we use according to the usage requirements. Types of DBMS Architecture are discussed here.
1-Tier Architecture
2-Tier Architecture
1-Tier Architecture
In 1-Tier Architecture the database is directly available to the user, the user can directly sit on the DBMS and use it that is, the client, server, and Database are all present on the same machine. For Example: to learn SQL we set up an SQL server and the database on the local system. This enables us to directly interact with the relational database and execute operations. The industry won’t use this architecture they logically go for 2-tier and 3-tier Architecture.
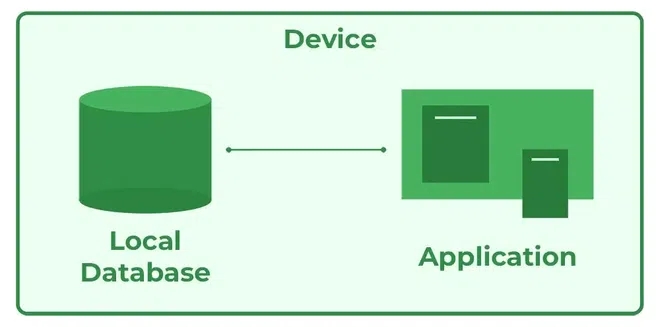
DBMS 1-Tier Architecture
Advantages of 1-Tier Architecture
Below mentioned are the advantages of 1-Tier Architecture.
Simple Architecture: 1-Tier Architecture is the most simple architecture to set up, as only a single machine is required to maintain it.
Cost-Effective: No additional hardware is required for implementing 1-Tier Architecture, which makes it cost-effective.
Easy to Implement: 1-Tier Architecture can be easily deployed, and hence it is mostly used in small projects.
2-Tier Architecture
The 2-tier architecture is similar to a basic client-server model. The application at the client end directly communicates with the database on the server side. APIs like ODBC and JDBC are used for this interaction. The server side is responsible for providing query processing and transaction management functionalities. On the client side, the user interfaces and application programs are run. The application on the client side establishes a connection with the server side to communicate with the DBMS. An advantage of this type is that maintenance and understanding are easier, and compatible with existing systems. However, this model gives poor performance when there are a large number of users.

DBMS 2-Tier Architecture
Advantages of 2-Tier Architecture
Easy to Access: 2-Tier Architecture makes easy access to the database, which makes fast retrieval.
Scalable: We can scale the database easily, by adding clients or upgrading hardware.
Low Cost: 2-Tier Architecture is cheaper than 3-Tier Architecture and Multi-Tier Architecture.
Easy Deployment: 2-Tier Architecture is easier to deploy than 3-Tier Architecture.
Simple: 2-Tier Architecture is easily understandable as well as simple because of only two components.
3-Tier Architecture
In 3-Tier Architecture, there is another layer between the client and the server. The client does not directly communicate with the server. Instead, it interacts with an application server which further communicates with the database system and then the query processing and transaction management takes place. This intermediate layer acts as a medium for the exchange of partially processed data between the server and the client. This type of architecture is used in the case of large web applications.
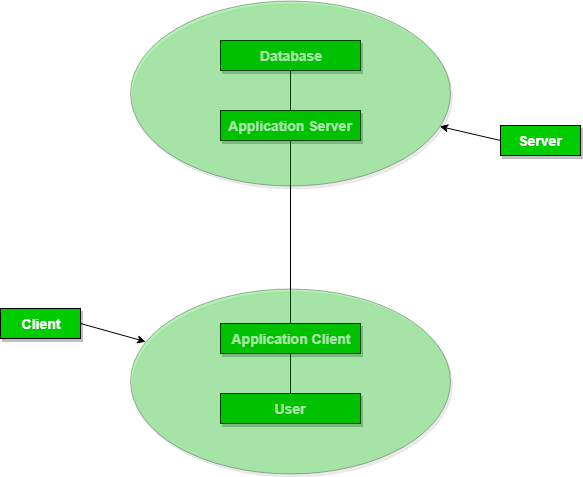
DBMS 3-Tier Architecture
Advantages of 3-Tier Architecture
Enhanced scalability: Scalability is enhanced due to the distributed deployment of application servers. Now, individual connections need not be made between the client and server.
Data Integrity: 3-Tier Architecture maintains Data Integrity. Since there is a middle layer between the client and the server, data corruption can be avoided/removed.
Security: 3-Tier Architecture Improves Security. This type of model prevents direct interaction of the client with the server thereby reducing access to unauthorized data.
Disadvantages of 3-Tier Architecture
More Complex: 3-Tier Architecture is more complex in comparison to 2-Tier Architecture. Communication Points are also doubled in 3-Tier Architecture.
Difficult to Interact: It becomes difficult for this sort of interaction to take place due to the presence of middle layers.
Last updated